
PCI Express is a serial connection that operates more like a network than a bus. It can make a computer faster, add graphics performance and replace the AGP slot. See how it works on the next few pages.
Advertisement

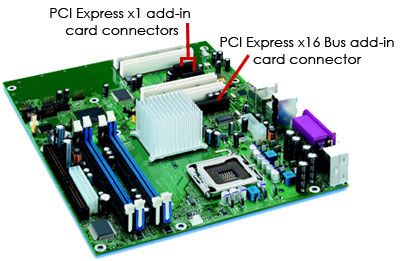
A x16 PCIe slot can accommodate far more data per second than current AGP 8x connections allow. In addition, a x16 PCIe slot can supply 75 watts of power to the video card, as opposed to the 25watt/42 watt AGP 8x connection.
PCIe lanes move packets of data at a rate of one bit per cycle.
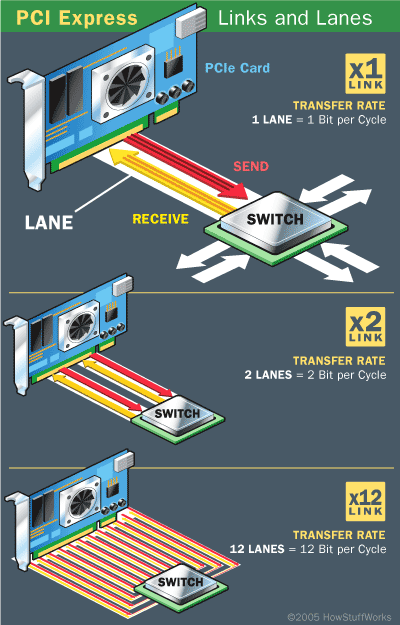
Each lane of a PCI Express connection contains two pairs of wires -- one to send and one to receive.
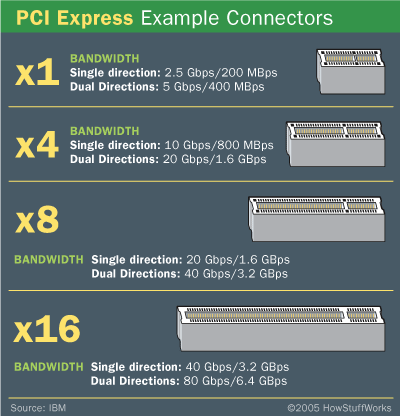
A x1 connection, the smallest PCIe connection, has one lane made up of four wires. A x2 link contains eight wires and transmits two bits at once, a x4 link transmits four bits, and so on. Other configurations are x12, x16 and x32.
Advertisement
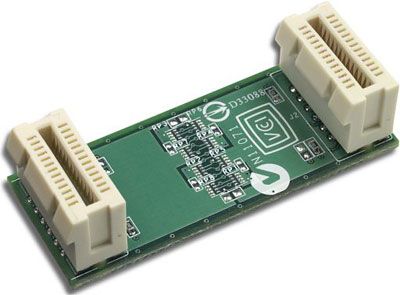
With an SLI-certified motherboard, two SLI graphics cards and an SLI connector, a user can put two video cards into the same system.
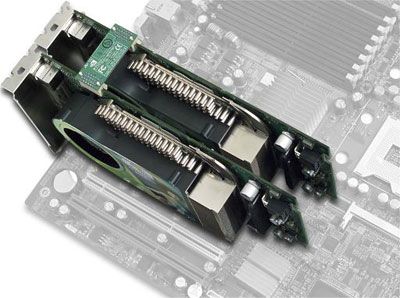
Alienware Video Array: Two off-the-shelf video cards combine with a Video Merger Hub and proprietary software. This system will use specialized cooling and power systems to handle all the extra heat and energy from the video cards.
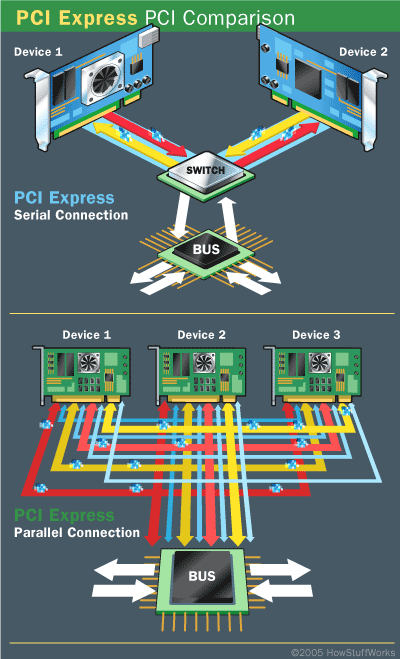
Devices using PCI share a common bus, but each device using PCI Express has its own dedicated connection to the switch. For more information, see How PCI Express Works.