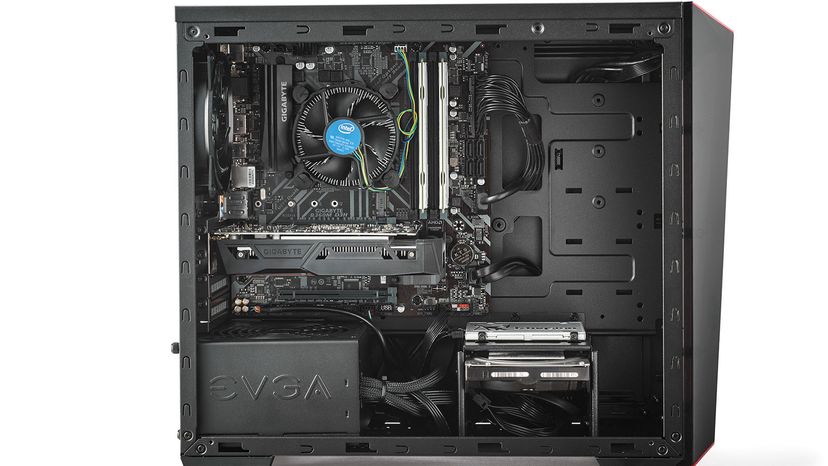
If there is any one component that is absolutely vital to the operation of a computer, it is the power supply. Without it, a computer is just an inert box full of plastic and metal. The power supply unit, also known as a PSU, converts the alternating current (AC) line from your home to the direct current (DC) needed by the personal computer. In this article, we'll learn how PC power supplies work and what the wattage ratings mean.
In a personal computer (PC), the power supply is the metal box usually found in a corner of the case. The power supply is visible from the back of many systems because it contains the power-cord receptacle and the cooling fan. A typical PSU will have integrated connectors to send power to the motherboard, microprocessors, and SATA storage. Laptops and mini-PCs usually have their power supplies separate from the computer assembly, instead of integrated into their charging cables.
Advertisement
Power supplies, often referred to as "switching power supplies", use switcher technology to convert the AC input to lower DC voltages. The typical voltages supplied are:
- 3.3 volts
- 5 volts
- 12 volts
The 3.3 and 5 volts are typically used by digital circuits, while the 12 volt is used to run motors in disk drives and fans. The main specification of a power supply is in watts. A watt is the product of the voltage in volts and the current in amperes or amps. If you have been around PCs for many years, you probably remember that the original PCs had large red toggle switches that had a good bit of heft to them. When you turned the PC on or off, you knew you were doing it. These switches actually controlled the flow of 120-volt power to the power supply.
Today you turn on the power with a little push button, and you turn off the machine with a menu option. The operating system can send a signal to the power supply to tell it to turn off. The push button sends a 5-volt signal to the power supply to tell it when to turn on. The power supply also has a circuit that supplies 5 volts, called VSB for "standby voltage" even when it is officially "off", so that the button will work.
Advertisement