Cities and Municipalities
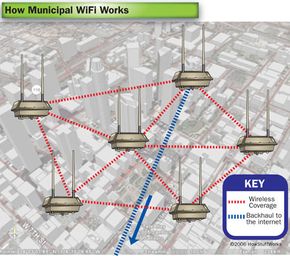
With wireless mesh networks, cities can connect citizens and public services over a widespread high-speed wireless connection.
A growing number of downtown areas are installing public WiFi hotspots. Mesh networks allow cities to inexpensively and simply link all those hotspots together to cover the entire municipality. Municipal networks aren't always created and maintained by the cities or communities themselves. Some are ad-hoc networks created by local residents. Others launch with funding from nonprofit or government projects. The U.S. State Department has funded mesh networks in some foreign locations to offer dissidents a way to communicate without their own government's surveillance.
Some advantages of open municipal mesh WiFi networks:
- Commuters can check their email on the train, in the park or at a restaurant.
- Public works officials can monitor the diagnostics of the city's power and water supply by installing wireless nodes in water treatment facilities, sewers and generators. There's no need to dig trenches to run cables.
- Public safety and emergency workers can access secure virtual networks within the larger network to keep communication lines open, even when regular phone or cellular service is down. With mesh nodes mounted on streetlights and stoplights, police and firefighters can remain connected to the network, even while moving.
Municipal Networks Have Expanded
MuniNetworks.org, a project of the nonprofit Institute for Local Self-Reliance, maintains a map showing hundreds of communities in the United States with municipal networks, many of which use mesh networking to distribute broadband access. Municipal mesh networks are not just available in the U.S. They're becoming popular around the world in places such as Berlin, Buenos Aires and Melbourne.
Mesh networks are even coming to neighborhoods through corporate channels. Retail giant Amazon is using its Ring branded smart home devices to create mesh networks between nearby houses. Announced in 2019, Amazon Sidewalk became active in summer 2021. Amazon's stated intent for the service is to support customers' smart home devices, and unlike municipal WiFi networks, Amazon Sidewalk's mesh network uses the 900 MHz spectrum to communicate.
Not all municipal wireless networks use mesh technology, however. Some use a technology called WiMAX, which has the ability to broadcast signals over large distances using powerful microwave transmissions. Other municipal networks use a combination of mesh, WiMAX and others.
Developing Countries
Wireless mesh networks are useful in countries without a widespread wired infrastructure, such as telephone service or even electricity. Solar-powered nodes can be connected to one cellular or satellite internet connection, which could keep a whole village online.
Isolated Locations
Even in developed countries, there are rugged locations too far off the grid for traditional high-speed internet service providers. Wireless mesh networks are being considered for these areas. A series of nodes would be mounted from the nearest available wired access point out to the hard-to-reach area.
Educational Institutions
Many colleges, universities and high schools are converting their entire campuses to wireless mesh networks. This solution eliminates the need to bury cables in old buildings and across campuses. With dozens of well-placed indoor and outdoor nodes, everyone will be connected all the time.
Mesh networks also have the capacity to handle the high-bandwidth needs required by students who need to download large files.
Schools can also rig their entire public safety systems up to their network, monitoring security cameras and keeping all personnel in constant communication in emergency situations.
Healthcare Facilities
Many hospitals are spread out through clusters of densely constructed buildings that were not built with computer networks in mind. Wireless mesh nodes can sneak around corners and send signals short distances through thick glass and other materials to ensure access in every operating room, lab and office.
The ability to connect to the network is crucial as more doctors and caregivers maintain and update patient information — test results, medical history, even insurance information — on portable electronic devices carried from room to room.
Hospitality and Temporary Venues
High-speed internet connectivity at hotels and resorts has become the rule, not the exception. Wireless mesh networks are quick and easy to set up indoors and outdoors without having to remodel existing structures or disrupt business.
Construction sites can capitalize on the easy set-up and removal of wireless mesh networks. Architects and engineers can stay wired to the office, and ethernet-powered surveillance cameras can decrease theft and vandalism. Mesh nodes can be moved around and supplemented as the construction project progresses.
Wireless mesh networks can be set up and torn down quickly in other temporary venues like street fairs, outdoor concerts and political rallies. And in Hong Kong, protesters have been using peer-to-peer mesh networks created by smartphone apps to avoid surveillance and to get around internet shutdowns.
Warehouses
There is simply no effective way to keep track of stock and shipping logistics without the handheld scanners used in modern warehouses. Wireless mesh networks ensure connectivity throughout a huge warehouse structure with little effort.