Bus Speed
A bus is a circuit that connects one part of the motherboard to another. The more data it can handle at one time, the faster it allows information to travel. The speed of the bus refers to how much data can move across the bus simultaneously.
In newer motherboards using PCIe, you might see bandwidth described in terms of numbers of lanes, which function like lanes on a street. Each lane has two pairs of wires, one for receiving information and the other to transmit. Unlike what you see on city streets however, the lanes are inside the bus. Each device needs enough lanes to manage the throughput it needs. If you're building a high-end gaming machine with a powerful graphics card, you'll want more lanes, but for a simple daily work computer you probably don't need as many.
Advertisement
Bus speed usually refers to the speed of the front side bus (FSB), which connects the CPU to the northbridge. FSB speeds can range from 66 MHz to over 800 MHz. Since the CPU reaches the memory controller though the northbridge, FSB speed can dramatically affect a computer's performance.
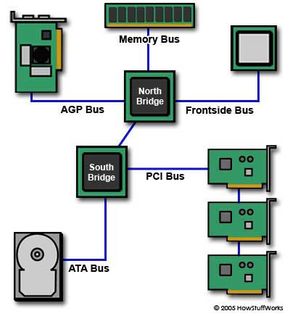
Here are some of the other busses found on a motherboard:
- The back side bus connects the CPU with the level 2 (L2) cache, also known as secondary or external cache. The processor determines the speed of the back side bus.
- The memory bus connects the northbridge to the memory.
- The IDE or ATA bus connects the southbridge to the disk drives.
- The AGP bus connects the video card to the memory and the CPU. The speed of the AGP bus is usually 66 MHz.
- The PCI bus connects PCI slots to the southbridge. On most systems, the speed of the PCI bus is 33 MHz. Also compatible with PCI is PCI Express, which is much faster than PCI but is still compatible with current software and operating systems. PCI Express is likely to replace both PCI and AGP buses.
The faster a computer's bus speed, the faster it will operate — to a point. A fast bus speed cannot make up for a slow processor or chipset.
Now let's look at memory and how it affects the motherboard's speed.