VLAN Trunking Protocol
The VLAN trunking protocol (VTP) is the protocol that switches use to communicate among themselves about VLAN configuration.
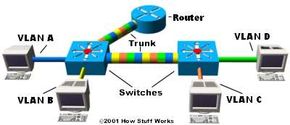
In the image above, each switch has two VLANs. On the first switch, VLAN A and VLAN B are sent through a single port (trunked) to the router and through another port to the second switch. VLAN C and VLAN D are trunked from the second switch to the first switch, and through the first switch to the router. This trunk can carry traffic from all four VLANs. The trunk link from the first switch to the router can also carry all four VLANs. In fact, this one connection to the router allows the router to appear on all four VLANs, as if it had four different physical ports connected to the switch.
Advertisement
The VLANs can communicate with each other via the trunking connection between the two switches using the router. For example, data from a computer on VLAN A that needs to get to a computer on VLAN B (or VLAN C or VLAN D) must travel from the switch to the router and back again to the switch. Because of the transparent bridging algorithm and trunking, both PCs and the router think that they are on the same physical segment!
As you can see, LAN switches are an amazing technology that can really make a difference in the speed and quality of a network.
For more information on LAN switches, networks and related topics, check out the links below.
Related Articles
More Great Links
- Webopedia: switch
- Cisco: Internetworking Technology Overview
- Cirrus: LAN Switch
- University of New Hampshire InterOperability Lab: Ethernet Tutorials and Resources
- Cisco: Understanding Spanning-Tree Protocol
- Cisco VLAN Roadmap
- VLAN tagging for linux
- Are there Vulnerabilities in VLAN Implementations?
- Ethernet Media Access Control
- Full Duplex Ethernet & Fiber Optic Cabling
- Layer 3 Switching Demystified