The use of fast Internet connections has grown rapidly over the last few years. As more people buy home computers and create home networks, the demand for broadband (high-speed) connections steadily increases. Two technologies, cable modems and Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL), currently dominate the industry.
While both of these technologies provide Internet connections that are many times faster than a 56K modem, they still are not fast enough to support the integration of home services such as digital television and video-on-demand.
Advertisement
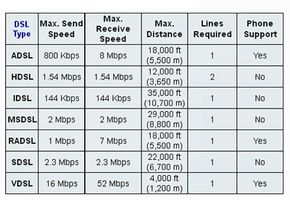
However, another DSL technology known as very high bit-rate DSL (VDSL) is seen by many as the next step in providing a complete home-communications/entertainment package. There are already some companies, such as U.S. West (part of Qwest now), that offer VDSL service in selected areas. VDSL provides an incredible amount of bandwidth, with speeds up to about 52 megabits per second (Mbps). Compare that with a maximum speed of 8 to 10 Mbps for ADSL or cable modem and it's clear that the move from current broadband technology to VDSL could be as significant as the migration from a 56K modem to broadband. As VDSL becomes more common, you can expect that integrated packages will be cheaper than the total amount for current separate services.
In this article, you'll learn about VDSL technology, why it's important and how it compares to other DSL technologies. But first, let's take a look at the basics of DSL.
A standard telephone installation in the United States consists of a pair of copper wires that the phone company installs in your home. A pair of copper wires has plenty of bandwidth for carrying data in addition to voice conversations. Voice signals use only a fraction of the available capacity on the wires. DSL exploits this remaining capacity to carry information on the wire without disturbing the line's ability to carry conversations.
Standard phone service limits the frequencies that the switches, telephones and other equipment can carry. Human voices, speaking in normal conversational tones, can be carried in a frequency range of 400 to 3,400 Hertz (cycles per second). In most cases, the wires themselves have the potential to handle frequencies of up to several-million Hertz. Modern equipment that sends digital (rather than analog) data can safely use much more of the telephone line's capacity, and DSL does just that.
VDSL could change the face of E-commerce by allowing all types of media to run smoothly and beautifully through your computer. Click here to learn more about E-commerce.
In the next section, we'll look at ADSL.
Advertisement