Computer Screens & Monitors
Many of us sit in front of a computer monitor every day. But how do monitors work? What do you need to look for in purchasing a new one?

How CD Burners Work

Why can I play some DVD movies but not others on my computer DVD-ROM?

Which Computer Keyboard Keys Wear Out the Fastest?

How the Xynergi Keyboard Works

How Does an Optical Mouse Work?

How 3-D PC Glasses Work
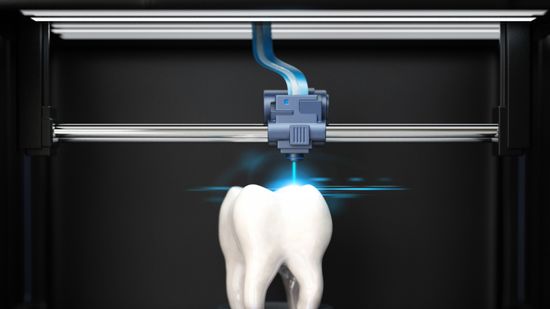
How Stereolithography Works: A 3D Printing Process
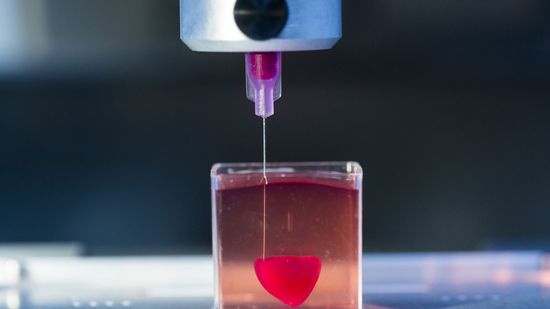
How Does a 3D Printer Work?

How Printer Ink Works

How Wireless Technology Changed Printing

How to Connect AirPods to a Laptop (Windows and Mac)

How to Connect AirPods to a PC

How to Move Pictures From a Memory Card to a PC or Laptop
Learn More
The future is now. Microsoft Surface tabletop allows multiple users to share and manipulate information on a tabletop computing interface. See how it works.
Transmissive film can make a LCDs display brighter and easier to read. Or it can keep others from reading your screen. See how it works.
By Dave Roos
Touch-screen monitors have become more and more commonplace as their price has steadily dropped. There are three basic systems that are used to recognize a person's touch -- learn how they work.
Advertisement
The next generation in computer displays gives you a full 180-degree field of view. Learn how the Elumens display works!
By Jeff Tyson
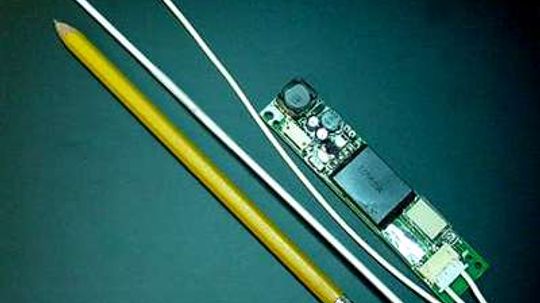
Fluorescent tubes and backlighting help make a computer's LCD screen bright and readable. Find out how these parts work together to keep your screen aglow.
Remember those faint horizontal lines on cathode ray tube computer screens? What caused them to appear?
Although Macintosh computers and UNIX workstations have sported dual screen connectivity for years, Windows was slower to progress. Find out how to hook it all up.
Advertisement
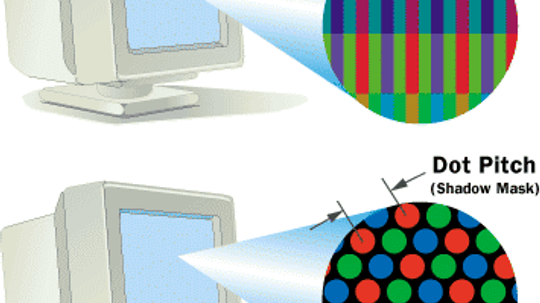
Because we use them daily, many of us have a lot of questions about our monitors and may not even realize it. What does "aspect ratio" mean? What is dot pitch? What does "refresh rate" mean? The answers just might help you make better use of your mon
By Jeff Tyson & Carmen Carmack
Dot pitch is measured in millimeters (mm), and a smaller number means a sharper image. How you measure the dot pitch depends on the technology used.