Internet Technology
We look to the Internet for news, socializing, shopping, research and more. From HTML code to instant messaging, we'll break down what's really going on whenever you log on, send an e-mail, visit a popular Web site or post to a blog.

The Truth About Cloud Storage and Its Future

5 Ways to Keep Your Information Secure in the Cloud

Are my files really safe if I store them in the cloud?

Can the Internet Break From Overuse?

Could an Attack on Undersea Cables Take Down the Internet?

Constellations of Internet Satellites Will Beam Broadband Everywhere
How to Recall an Email in Outlook or Gmail

What Does CC Mean in Email?

How to End an E-Mail: 21 Professional and Personal Sign-Offs

How Do Search Engines Work? All About Ranking and Bidding

How to Access the Dark Web

How to Change the Language in Google Chrome

4 Most Secure VPN Option to Keep Your Internet Activity Private

7 Most Secure Browser Options for Privacy-Minded Individuals

Looking for a Search Engine That Donates to Charity? Here Are 10
Should You Use Facebook or Google to Log In to Other Sites?
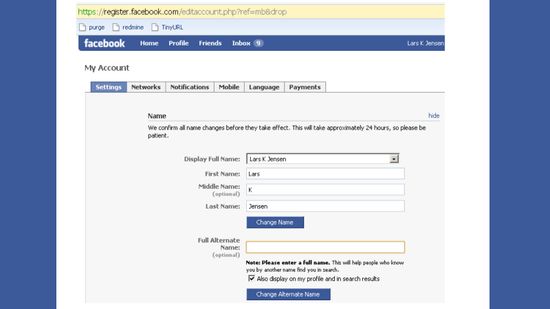
How to Change Your Name on Facebook

How to Deactivate Facebook

Google Easter Eggs: Sweet Treats Hidden in Plain Sight

10 Reasons Why You Should Care About Net Neutrality

WiFi Extender vs. Booster: What's the Best Choice for You?

Does Weather Mess With Your Internet Connection?

Why Does My WiFi Keep Disconnecting? 6 Easy Fixes
Learn More / Page 12
These days, you can find animated figures all across the Internet! Ready to give life to your own creations? Learn about dynamic HTML, animated GIFs, Java, Shockwave and Flash animation techniques.
By Tom Harris
Do you get the shakes when you're offline for more than 10 minutes? The wireless Internet lets you browse Web pages from a cell phone or PDA. Learn about the Wireless Application Protocol that makes it possible to surf on the go.
By Jeff Tyson
The funny little "a" with its tail circling back around it is probably one of the most commonly used symbols today. So it is truly amazing to learn that there is no official, universal name for it.
Advertisement
To make it easier to pick out a particular link from your list of favorites, Internet Explorer versions 5.0 and higher include custom bookmark icons for some sites. Learn how they do it and how these icons make your web surfing easier.
Internet search engines are special sites on the Web that help people find information stored on other sites. There are differences in the ways various search engines work, but they all perform three basic tasks.
Learn how a cable modem works and see how dozens of television channels plus any Web site out there can flow over a single coaxial cable into your home.
You can put anything you want on a Web page, from family pictures to business information, to your random thoughts and musings. Learn how to create, upload and promote your pages so they're available all over the world.
Advertisement
Banner ads generate a big part of the revenue for many Web sites. Learn how banner ads work, how much they cost and how much you might earn if you put them on your Web page.
By Tom Harris
When you connect to the Internet, you might connect through a regular modem, a local-area network connection, a cable modem or a digital subscriber line (DSL) connection. DSL is a very high-speed connection that uses the same wires as a regular telephone line.
One of the greatest things about the Internet is that nobody really owns it. It is a global collection of networks, both big and small, that connect together in many different ways to form the single entity that we know as "the Internet." How is this possible?
What's so special about a T1 line? It means the phone company has brought a fiber optic line into your office that can carry data at a rate of 1.544 megabits per second!
Advertisement
It's a frustration most of us encounter daily - the broken link. It's especially annoying when you're really looking forward to that page you expect to load! Find out what (besides human error) creates broken links.
Once you spend a good deal of time on the Web, you start learning the language of internet addresses. Have you come across sites that use something in place of www? (Hint: you're on one now!)
Are you ready to get your brilliant idea online and active? Here's the breakdown of what you'll need to do.
While .html may be the most common file extension, what do the others mean? What about .htm, .asp or .php?
Advertisement
When you try to leave a Web site, either by using the Back button or by closing the browser window, the site reappears in a new window. Or maybe the site pops up in three or four new windows when you try to leave it. What's going on here?
How do large Web sites handle the load of millions of visitors a day? Learn about Domain Name Servers and load balancing switches.
"Howstuffworks.com" is a domain name. The com portion of the name is called the top-level domain name. See the other standard top-level names and who uses them.
Cookies have, for some reason, gained a rather sinister image, but a cookie is just one or more pieces of information stored as text strings on your machine. Find out how they work and how they got their dangerous image.
Advertisement
One of the most unique business models spawned by the Web is the Application Service Provider. Learn all about this innovative Internet-based software-publishing model.
When you type a URL into your web browser's address bar, the correct page appears as if by magic (provided you typed it correctly). Is it the work of sorcery? Nope! Domain name servers are handling all the data behind the scenes.
Much of the world still uses a standard modem to connect to the Internet. In this article, we'll start with the original 300-baud modems and progress all the way through to the ADSL configurations.